Facebook has a shiny new bridge to sell you.
The preposterously self-described “privacy-focused social platform” announced the latest addition to its family last week in the form of the video chatting tool Messenger Rooms. However, despite the company’s assurances that it built Rooms with “privacy and security in mind,” there are plenty of reasons to be skeptical of Facebook’s latest foray into your life.
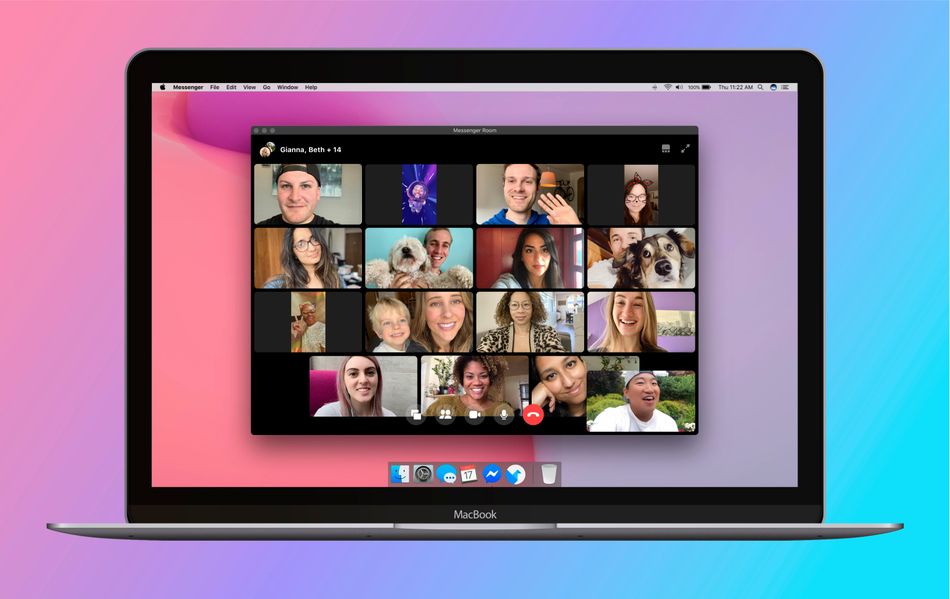
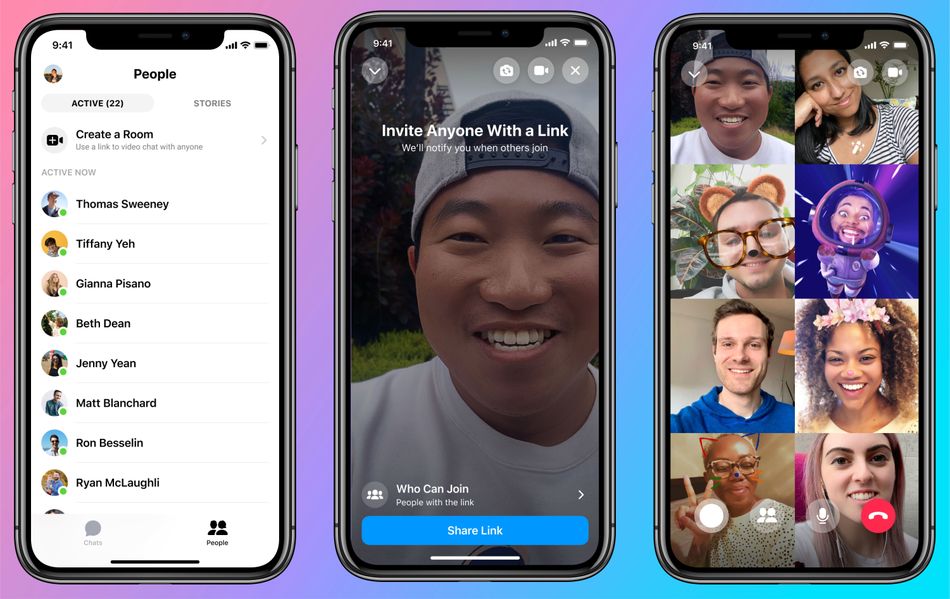
On the surface, Messenger Rooms, which according to Facebook will be available globally in “the coming weeks,” appears much like its competitor Zoom. The service allows anyone with a Facebook account to create a so-called room that others can join. It will support up to 50 simultaneous participants, and offers the popular tile view.
It also comes with a lot of red flags.
For starters, it’s worth considering the big picture. Facebook, according to FTC charges, has a long history of “deceiving users” regarding its handling of their data. According to Ashley Boyd, the Mozilla Foundation’s vice president of advocacy, Facebook’s past actions should inform our understanding of the company and its products today — even the new ones like Messenger Rooms.
“With Facebook, we are always concerned about how much data they collect on users and how they handle that data,” she told Mashable over email. “We know Facebook has been careless with users’ data in the past.”
Careless, of course, might fairly be considered an understatement. Data breach after data breach, privacy scandal after privacy scandal after privacy scandal, Facebook has repeatedly demonstrated its inability or unwillingness to fully secure the data of its billions of users. Every product it pushes going forward, every promise about protecting your data it makes, must be considered in this light.
Encryption
So, let’s consider Messenger Rooms. For starters, the video chat service is not end-to-end encrypted. Facebook admits as much, implying that it’s simply too difficult to protect calls in such a manner at this time.
“While there are significant challenges to providing end-to-end encryption for video calling with large groups of people,” explains a Messenger Rooms privacy page, “we’re actively working toward this for Messenger and Rooms.”
It’s worth noting that Apple’s FaceTime, which allows users to “invite up to 32 participants,” is end-to-end encrypted.
Facebook claims it does employ some form of encryption for Messenger Rooms — just not the same high standard employed by competing products like FaceTime and Signal.
“Rooms is built on Messenger, so it uses the same technology to encrypt a video and audio conversation between people as it travels from their devices to our servers that we have placed in only a handful of countries that have strong rule of law,” reads the Messenger Rooms privacy page.
Because the calls are not end-to-end encrypted, as calls pass through Facebook’s servers the company has the technical ability to access their content — or hand that content over to law enforcement.
In January of this year, Wired reported that — despite promises made by Mark Zuckerberg in March of 2019 — Facebook was in fact still “years away” from a Messenger that is end-to-end encrypted by default.
So, you know, perhaps don’t expect Messenger Rooms to have that level of security any time soon.
Facebook is watching, just not in the way you think
Facebook is a data-consuming behemoth. Its mission, other than making money, is to gather as much information as possible on its users in order to ply them with ever more micro-targeted ads.
And while Facebook promises that it will not watch or listen to your conversations in Messenger Rooms, that doesn’t mean it isn’t tracking them. Facebook has long been known to collect metadata — information like who you speak with, when, and how frequently — even if (in some cases) it doesn’t technically look at the content of those messages.
“As with other parts of Facebook, we collect data from Rooms regardless of whether you joined through one of our apps or without logging into an account,” explains Facebook.
Why does metadata matter? Well, if someone knows you visited the Facebook page of an anti-sexual violence organization like RAINN, and then shortly after the page of a local Planned Parenthood clinic, for example, that person can make an informed guess about intimate specifics of your life.
Now, imagine seeing ads on your Facebook feed based on that metadata.
When asked over email whether or not Facebook uses data collected during Messenger Rooms conversations for advertising, Facebook spokesperson Liz Sweeney responded simply by stating that “we don’t watch or listen to Rooms calls, so audio and video from Rooms won’t be used to inform ads.”
In other words, she studiously avoided answering the question.
Ripe for abuse
When it comes to using Messenger Rooms, it’s not just Facebook’s prying eyes you’ll need to watch out for. The service is practically teed up for its own version of zoombombing.
For the blissfully unaware, zoombombing is when uninvited individuals crash a video chat and spam it with porn, racist, sexist, or violent content. As PCMag reported in late March, this form of harassment doesn’t stop at simply disrupting the zoombombed meetings. Those engaging in that form of harassment have recorded video of their antics and later posted those videos online. When the zoombombed meetings being posted are that of elementary school classrooms, the entire thing takes on an exceptionally unpleasant pale.
It is with this in mind that we look at the security of the Messenger Rooms themselves.
Notably, Messenger Rooms does not offer the option to password protect your group video call. Let that sink in. Instead, Facebook gives the creator of the so-called room the ability to lock it.
“Rooms can be locked or unlocked once a call begins,” explains the Messenger Rooms privacy page. “If a room is locked, no one else can join, except a Group admin for rooms created through a Group.”
This is very different than a password-protected group call. In Facebook’s rooms, the only way friends and family can join a call late or trickle in after it started is if the room creator leaves the room permanently unlocked or temporarily unlocks it at those friends’ requests.
Which, OK, that might not be a huge issue were it not for the fact that this directly contradicts CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s main selling point for Messenger Rooms.
“I don’t really think there’s anything today that you can display on an ad hoc basis that you’re hanging out and have whoever wants to join you over video,” he told the New York Times.
In case that’s not clear enough, Facebook reiterates a similar point in its blog post announcing Messenger Rooms.
“You can start and share rooms on Facebook through News Feed, Groups and Events, so it’s easy for people to drop by.”
In order for this serendipitous fantasy to occur, you have to leave your Messenger Rooms call unlocked. That means it’s open to being roombombed.
It’s also worth noting that Messenger Rooms does not advertise itself as having the equivalent of Zoom’s waiting room feature. That is to say, each new participant does not appear to need to be individually admitted by the person who initiated the Messenger Rooms room. Instead, it seems there are a host of privacy settings that are bound to confuse meeting hosts.
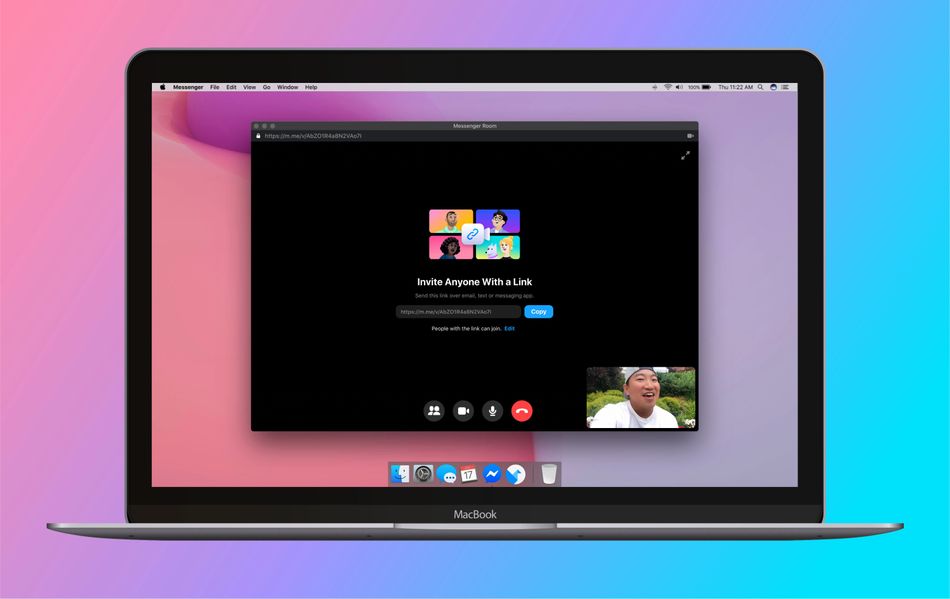
“The person who creates the room controls the settings for who can join, how easy a room is to find and whether to enable or share a link,” notes Facebook. “The default privacy settings were designed to be consistent with what you’d expect for where you create a room. For example, rooms you create through a Facebook Group are open by default to members of that Group.”
Got that? Notice that in the above sample image, provide by Facebook, the Messenger Rooms setting is set to “anyone with the link can join.”
Importantly, you do not need a Facebook account to join a Messenger Rooms call. While this is great for those who want to invite their privacy-conscious friends to Messenger Rooms calls, it also makes it a lot easier to anonymously roombomb said calls. While it’s hard to say for sure until Messenger Rooms launches and we get a chance to actually try the thing out, it seems that all bad actors would need to do is drop a Messenger Rooms link in a Tor browser before harassing everyone on the call.
A host can kick people out of the room, which automatically locks it, but then the host must unlock the room to let anyone else in.
SEE ALSO: How to use Jitsi Meet, an open source Zoom alternative
Facebook did at least think to make the Messenger Rooms links hard to guess with “a string of random characters and digits at the end, with numbers and letters in different cases.” This may prevent the Messenger Rooms equivalent of war dialing, but it doesn’t prevent people from intentionally spreading Messenger Rooms links or searching for open Messenger Rooms to crash on services like Google or Twitter.
Don’t settle
Facebook’s checkered past full of privacy abuses should have long ago rendered it as your last choice for a communications tool, not your first. Remember, there are other options.
Sure, Facebook talks a big game on respecting your privacy — and that hasn’t changed with its latest offering of Messenger Rooms. However, if you believe that, then I also have a bridge to sell you.